λ red mediated ssDNA gene modification
Background
Protocol designed based on 3/16/11 Court Lab Protocol (which is available here) with Barrick lab specific modifications. Modifications include:- Detailed description of primer design
- Protocol streamlined for 2 electroporations for single base mutation
Before Starting
Design/Order Oligos
- A minimum of 6 oligos must be ordered for each mutation. (2 mutation oligos, 2 screening oligos, 1 sequencing oligo, and 1 common oligo)
- Mutation Oligos:
- 2 different 71bp oligos will be needed for each mutation. Oligo 2 will have your mutation with 35bp of background on each side, and Oligo 1 with that mutation plus 2 bp mutated to random sequence on each side of your mutation.
- Following examples based on 1bp SNP. b = background, M = mutation of interest, R = Random mutation, can be any single base substitution, but not degenerate.
- Mutation Oligo 2: bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb bb M bb bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
- Mutation Oligo 1: bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb RR M RR bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
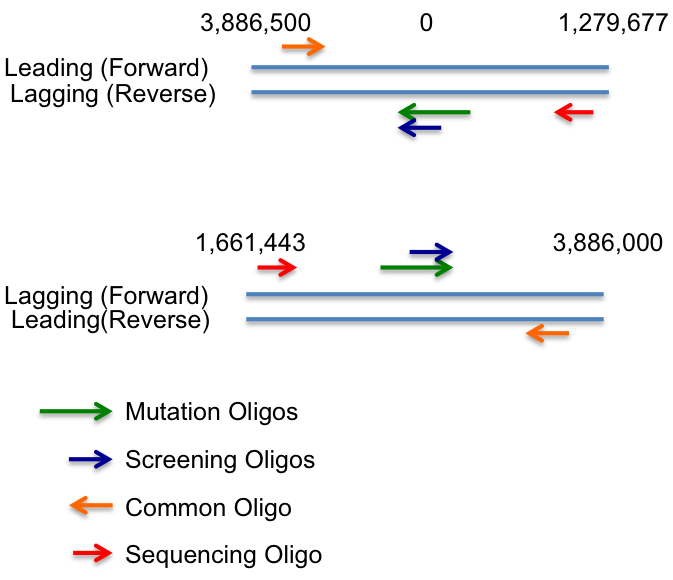
- Mutations MUST be placed on the lagging strand.
- For E. coli REL606 (and other B strains) origin of replication is at ~10:00 not 12:00 (3886105-3886336). Therefor:
- If mutation location between ~ 3,886,500 and ~ 1,279,677 : design against reverse strand
- If mutation location between ~ 1,661,443 and ~ 3,886,000 : design against forward strand
- If mutation location between ~ 3,886,000 and 3,886,500 or ~1,279,500 and 1,662,000 it's probably best to try both strands and see which is better. Expect 100+ fold increase in efficancy for lagging strand.
- For E. coli REL606 (and other B strains) origin of replication is at ~10:00 not 12:00 (3886105-3886336). Therefor:
- Mutation Screen Oligo:
- Primers used for screening colonies for presence of transformants
- Should be ~20bp long, amplicon of ~150+ bp, and one primer must have 3' bases as mutations of interest.
- Mutation Screen 2: bbbbbbbbbbbbbbb bb M bb
- Mutation Screen 1: bbbbbbbbbbbbbbb RR M RR
- Both screen's can be done with a common primer at least 150 bp away on the opposite strand.
- Primer can also be used for sequencing oligo
- Mutation Sequencing Oligo:
- Primer to be used for final sequencing to verify mutation on correct background.
- Primer should be ~20bp long, ~150+ bp upstream of Mutation screen oligo.
Make λ red electrocompetent cells
- Make the line you wish to have your mutation of interest electrocompetent
- ProtocolsElectrocompetentCells
- Transform λ red plasmid into cells and select with appropriate antibiotic.
- pKD46 = AmpR & 32+ temperature sensitive replication
- pKD78 = CamR & 32+ temperature sensitive replication
- ProtocolsElectrocompetentCells Bottom section, but outgrowth MUST be done at 30C
- Make new line (background of interest with λ red plasmid) electrocompetent.
- Must induce λ red proteins before centrifigation.
- See ProcedureGenomeModificationDatsenkoWanner Day 2 for detailed induction information.
Day 0:
- Thaw 50 μL aliquot of electrocompetent cells on ice.
- Transfer cells to electroporation cuvette.
- Add ~100ng of Mutation Oligo 1 to pre-chilled cuvette.
- M.W. of ssDNA = (# nucleotides x 303.7) + 79.0. Therefore assuming 71 nucleotides, MW ~= 21642.41.
- Typical dilution of oligos is 100μM. Therefore ~2164 ng/μL.
- Working stock is 10μM. Therefore ~216ng/μL
- Therefore use ~0.5μL
- Pipette gently but thoroughly
- Do not vortex
- Use filter tips if working doing multiple mutations at once
- Electroporate, and immediately add 1ml of room temperature LB to cuvette.
- If preparing multiple samples, add LB before doing next electroporation.
- Cuvette with LB can be left at room temperature while rest of electroporations are finished.
- Transfer all liquid from cuvette to sterile tube for 30C outgrowth.
- If no selectable phenotype, 30 minutes is best.
- Explanation: Cells typically have 4-8 copies of the chromosome per cell when recombination takes place, but recombination will typically only take place on a single strand. 30 minutes of outgrowth allows the cells to recover, but chromosomes will not yet have segregated. Colonies will therefore be a mixture of recombinant and parental cells, with percentage of recombinant cells being between ~25% and 12.5%. Colonies that initially test present for transformants can then be streaked for single colonies which will be found at between 25 and 12.5%. Comparatively if chromosomes allowed to segregate, 4 to 8 times more colonies will need to be screened to find a single transformant.
- If mutation causes selectable phenotype, more than 2 hours of outgrowth should be performed in 10mL LB.
- If no selectable phenotype, 30 minutes is best.
- Dilute cells 1x10-4 to 1x10-6, and plate ~100μL on LB + antibiotic
- Allow plate to incubate overnight at 30C.
- Warning: lambda red plasmid is temperature sensitive above 32.
Day 1: Initial PCR Screening
- PCR with Mutation Screen Oligo 1 and Common oligo.
- Because the 3' mutation screen oligo will only bind to DNA that has been mutated, presence of a band signifies recombination.
- Likely that the brighter the band, the better candidate (ie greater percentage of cells recombinants).
- 30 cycles of standard colony PCR conditions acceptable.
- Initially test 40 colonies is recommended.
- Be sure to either patch cells or store in small amount of saline.
- If cells patched, allow to grow overnight and re-plate for single cells following day.
- Positive 2-3 positive colonies should be spread for single cells and incubated overnight at 30C on LB with antibiotic.
Day 2: Confirmation Screening
- Single colonies from plates should be subjected to the same protocol as was used on Day 1.
- Need experimental validation: 20-30 colonies should be sufficient to screen.
- Positive colonies should be used to inoculate LB+antibiotic overnight 30C cultures.
- 1 or 2 colonies should be sufficient
- Positive colonies can be PCR'd with common primer and sequencing primer and sent for sequencing off either primer if desired.
- Should not be necessary under normal circumstances.
Day 3: Fixing 4 bp mutation
- Make freeze down of overnight culture, this is an intermediate with a 5bp mutation.
- Make cells electrocompetant as previously being sure to induce the λ red proteins.
- Electroporate as in Day 0, but use Mutation Oligo 2.
Day 4: Background screen
- Repeat Day 1 protocol using Mutation Screen oligo 2 rather than 1.
Day 5: Final screen and sequencing
- Repeat Day 2 protocol.
- Positive colonies should be used to inoculate o/n cultures. These should contain the correct single base mutation.
- Additional sequencing PCR needs to be preformed. This should be using common primer and sequencing primer.
- Submit sample for sequencing with either primer.
| I | Attachment | History | Action | Size | Date | Who | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Recombineering.png | r1 | manage | 60.4 K | 2013-03-28 - 18:26 | DanielDeatherage |
Barrick Lab > ProtocolList > ProtocolsSsdnaRecombination