Megaprimer whole plasmid cloning
aka MEGAWHOP cloningaka Overlap Extension PCR cloning
We describe two approaches to MEGAWHOP in this protocol page.
Approach 1:
Adapted from Bryksin AV, Matsumura I. 2010. Overlap extension PCR Cloning: a simple and reliable way to create recombinant plasmids. Biotechniques.48(6):463-5.
Purpose
To insert a DNA sequence into a plasmid without restriction enzymes.Experimental Steps
- Create primers that amplify region of interest and hybridize with target plasmid
- Perform a Phusion PCR with primers using the region of interest as template
- Perform a second Phusion PCR using the products of the first PCR and the target plasmid as template
- Digest Second PCR with Dpn1 to remove parental plasmid
- Transform in E coli
Designing Primers
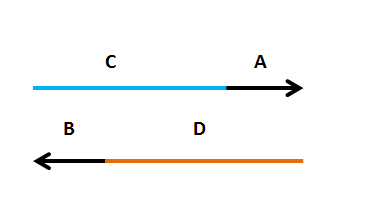 Primers need to have two components
Primers need to have two components - a region that amplifies the insert (A(or B), 20-25nt)
- a region that targets the new plasmid (C(or D), 30-40nt)
PCR Insert
Use standard 25ul Phusion (or other high fidelity polymerase) protocol- PCR 1(25ul reaction)
- 5 ul 5x Buffer
- 1.5 ul dntps
- 1.25 ul primer (A+C)
- 1.25 ul primer (B+D)
- x ul template plasmid (<250ng)
- ddH20 to 24.5 ul
- then add 0.5 ul Phusion
PCR Recombinant Plasmid
Use modified 10ul Phusion (or other high fidelity polymerase) protocol- 2 ul 5x Buffer
- 1 ul dntps
- 500 ng PCR insert product (Note, for optimal results, have a 250-fold molar excess of your megaprimer to your target plasmid).
- ~10 ng target plasmid
- ddH20 to 9.5 ul
- then add 0.5 ul Phusion
- 5 ul 5x Buffer
- 0.5 ul dntps
- 1 ul DMSO
- 100 ng PCR insert product
- 25 ng target plasmid
- ddH20 to 25 ul
- then add 0.25 ul Phusion
Digest
Once the reaction is complete, digest the Recombinant Plasmid PCR product with 0.5 ul Dpn1 at 37°C for one and a half hours to remove parental DNA. DpnI DigestTransform
Heatshock 5ul of the Dpn1-digested MEGAWHOP reaction mixture into 25ul of chemically competent E coli.Example
Change the promoter for sgRNA using MegaWHOP. Template sequence: https://benchling.com/s/g4S95i24 Primers:- T5-sgRNA-F: 5' CCGATAATTGCAGACGAACG cgcccttcccaacagttgcc3'
- T5-sgRNA-R:5' TATTCTGGTGGAACTGGATG tgaatctattataattgtt 3'
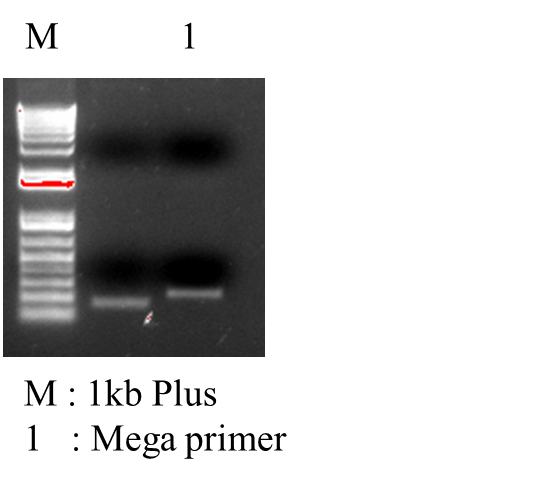 *PCR Recombinant Plasmid:
*PCR Recombinant Plasmid: 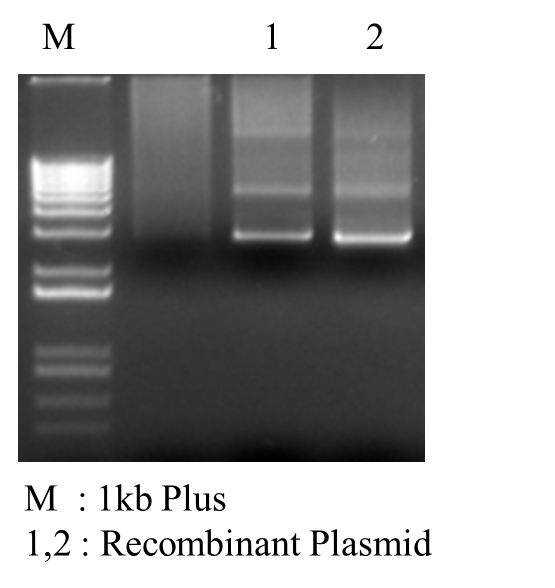
Approach 2:
Introduction
This protocol was inspired (after failed site directed mutagenesis attempts using Quikchange) by the protocol listed here at the Colgate website here. There are several other method papers that describe this (or variant) MEGAPRIMER and MEGAWHOP protocols, there is one here and the original here.This technique is useful for introducing single base pair, single amino acid, or multiple changes into a gene residing on a plasmid that you already have. In short, one mutagenic primer is paired with a standard primer to create a “Megaprimer” product that contains your mutation(s) of choice, is 200-400 bp long, and contains at least >=15 bp of homology on each end to your template plasmid. (You could, of course, just order a gene block with of this size containing all of your desired mutations and use it as a megaprimer). This megaprimer is purified and then used as primer with the template plasmid in a second PCR whole plasmid (Megawhop) reaction. This PCR product is cleaned up and transformed into competent cells to yield your desired mutation.
Required Materials
Template PlasmidCompetent Cells
PCR Reagents
Culturing Materials (>= 4 plates with appropriate antibiotics for transformations)
Sequence of desired mutation
Primer Upstream of Desired mutation
Procedure
1. Design a mutagenic primer with your desired mutation. Ensure at least 15 base pairs of homology downstream of your mutation.2. Create your megaprimer by running PCR using your upstream primer and designed primer with a standard Phusion protocol. Your template is your unmutated gene product. 2x 50 uL reactions are sufficient. This megaprimer will contain your desired mutations.
These steps have worked:
- Denature at 98 deg for 1 min.
- 30 cycles of:
- 98 deg for 30 sec
- 62 deg for 30 sec
- 72 deg for 15 sec
- 72 deg for 5 min
4. Use this purified megaprimer product and your template plasmid in a 2nd PCR (2x 50 uL reactions). Your control in this reaction is a reaction without your megaprimer from the previous step. Use commercial Phusion for this reaction (or other super high fidelity polymerase). Each tube should contain very little template plasmid (1 uL or 50 ng) and 5 uL of your purified megaprimer product. Concentrations for the rest of your PCR reagents are standard.
These steps have worked:
- Denature at 98 deg for 2 min
- 30 cycles of:
- 98 deg for 1 min
- 62 deg for 30 sec
- 72 deg for 3 min (based on a plasmid size of 5kb, you should adjust accordingly)
- 72 deg for 5 min
6. Optional You can run 5uL of your completed PCR reaction on an agarose gel and compare it to (1) your control reaction and (2)an unreacted mixture of the PCR components. You should see a faint band at your expected plasmid size only in your primer-containing reaction (DpnI should digest the template in both reactions).
7. PCR Cleanup both your sample and control reactions.
8. Transform 1-2uL of each reaction into competent cells using standard electroporation or chemical transformation protocols.
9. Plate dilutions of both reactions on appropriate antibiotic plates for selection.
10. If your sample shows more colonies than your control, the process was likely successful. Pick 3 clones to make stocks and send for sequencing (link)
Barrick Lab > ProtocolList > MEGAWHOP